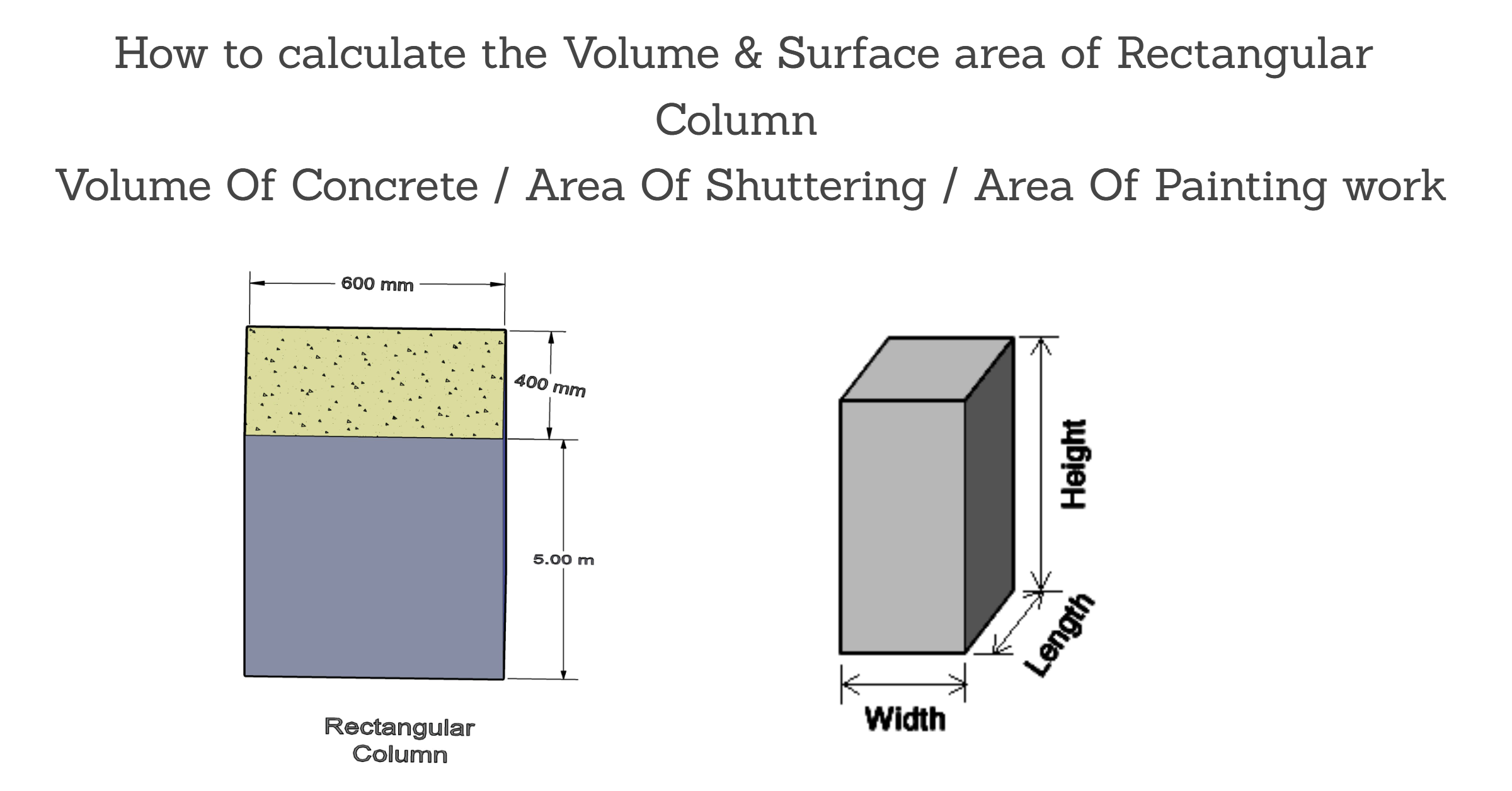
Mathematical symbols are important tools that help us to understand and solve math problems, also its used find or solve the relationships, and operations in mathematics universally. the following symbols are used commonly in mathematics
Addition (+), Subtraction (−), Multiplication (× or *), Division (÷ or /) – These symbols called as basic arithmetic operations.
Summation (∑), Integral (∫), Square Root (√), Factorial (!), Pi (π) – These symbols called as advanced mathematical operations and constants.
Equal to (=), Not equal to (≠), Approximately equal to (≈), Greater than (>), Less than (<), Greater than or equal to (≥), Less than or equal to (≤) – These symbols called as comparison operators and mathematical relationships
Empty set (∅), Infinity (∞), Plus-minus (±) – These symbols are used in set theory and general mathematical notation
Perpendicular (⊥), Angle (∠) – These symbols are commonly used in geometry and trigonometry.
Alpha (α), Beta (β), Gamma (γ), Delta (Δ or δ) – These Greek letters are used in various mathematical contexts, such as variables, constants, and functions.
Logarithm (log), Product notation (∏) – These symbols called as logarithmic functions and product summation.
The Following article we descripted the Mathematical Symbols with explanation
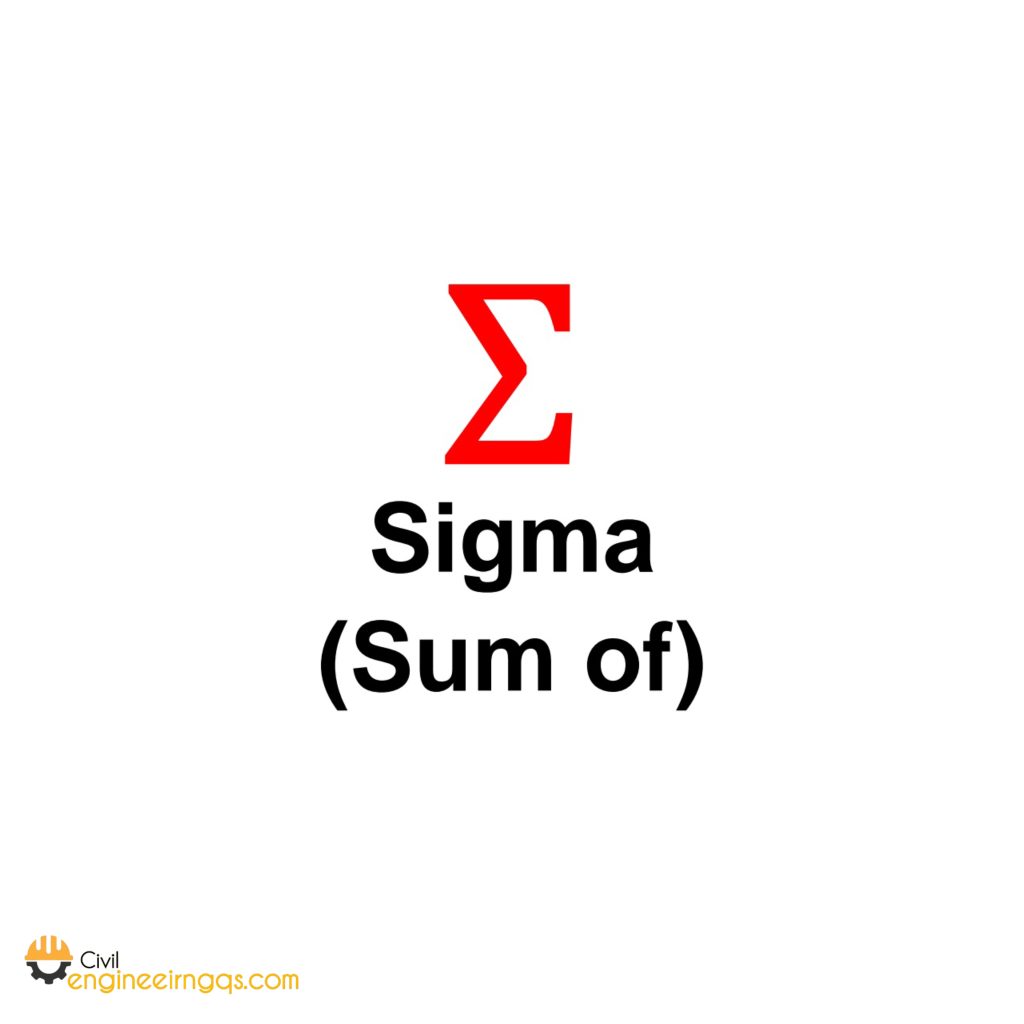
Σ (Sigma): Indicates the sum of a series of terms
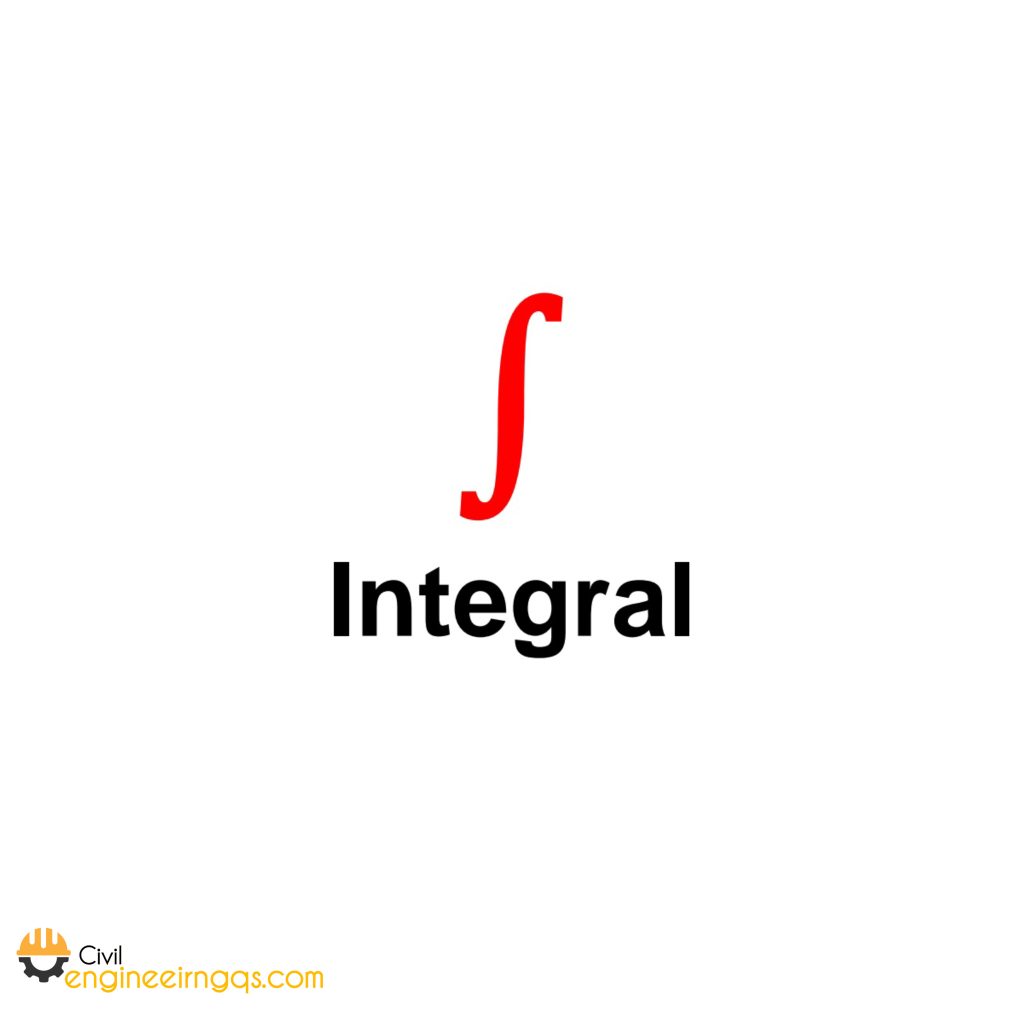
∫ (Integral): means it finds the total area under a curve.
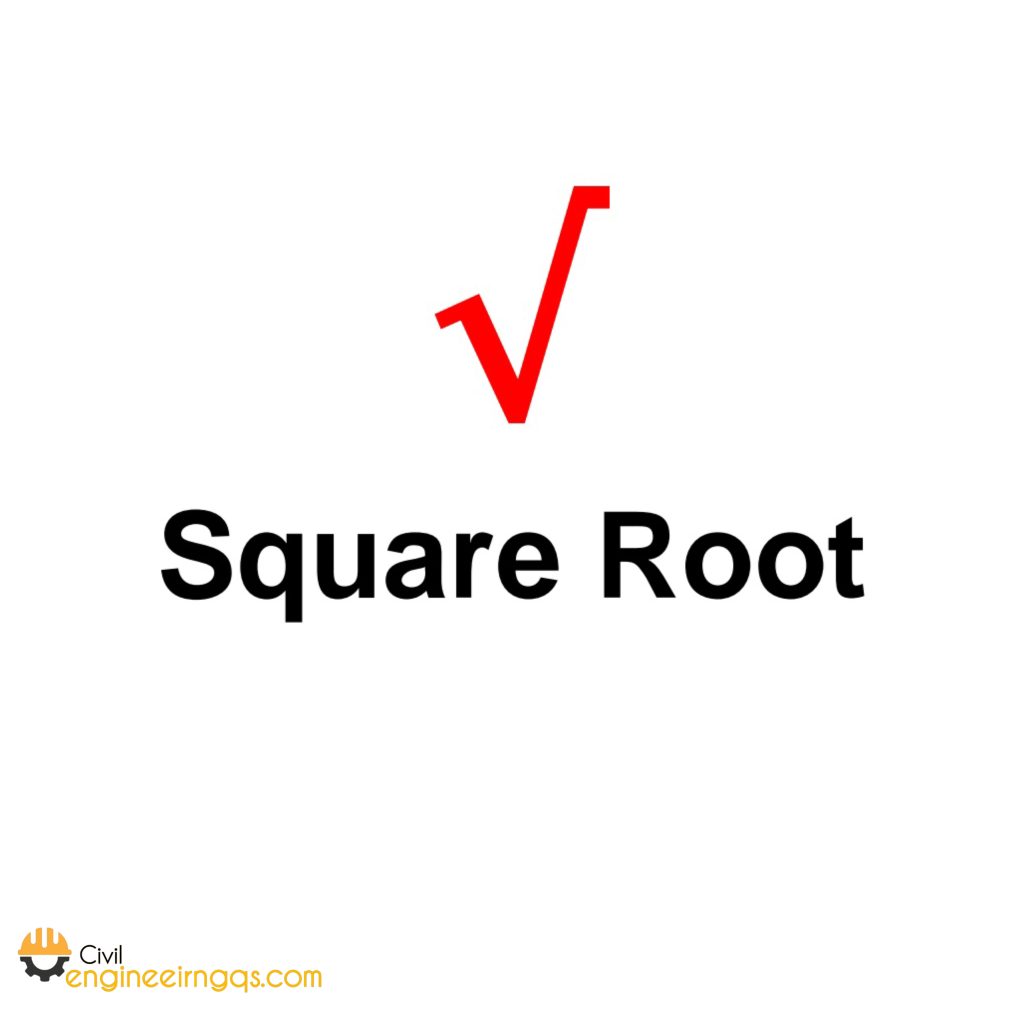
√ (Square Root): The number that, when squared (multiplied by itself), equals the original value.

π (Pi): Represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159.
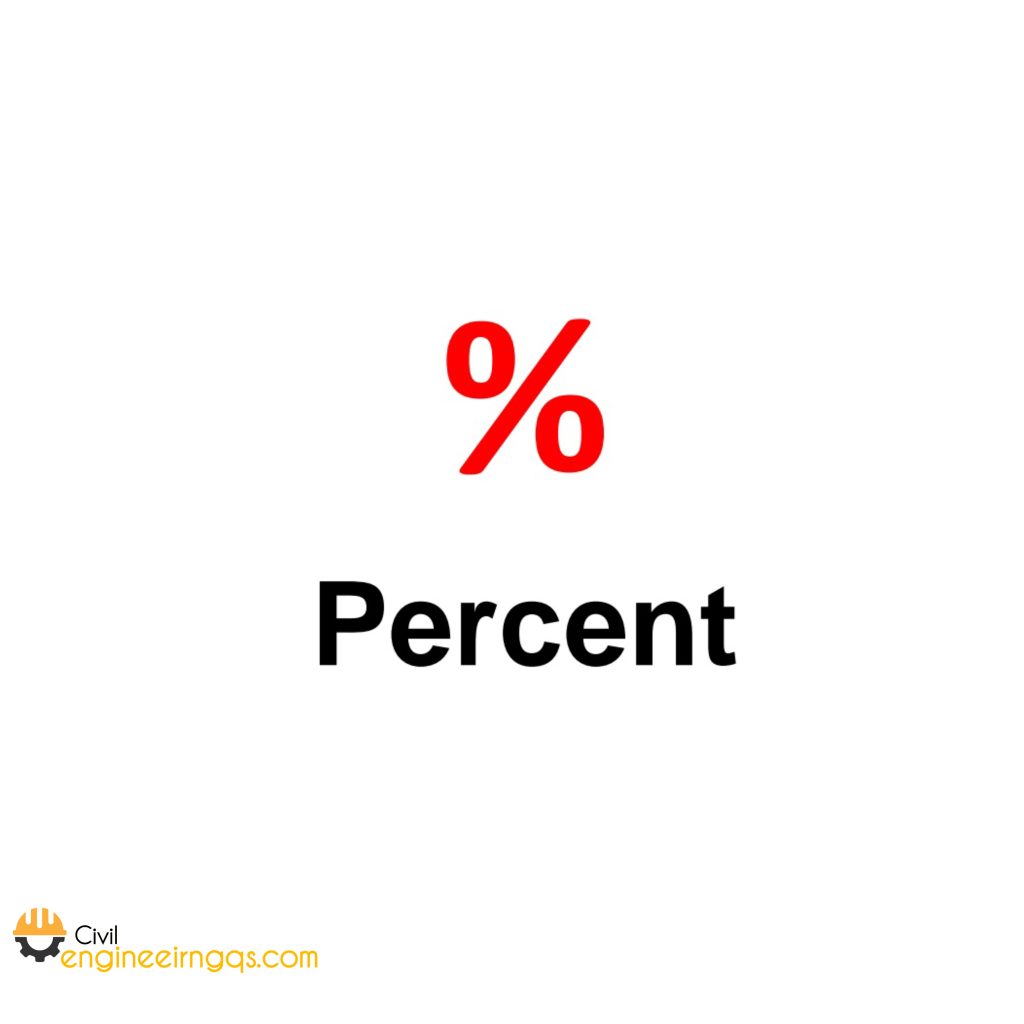
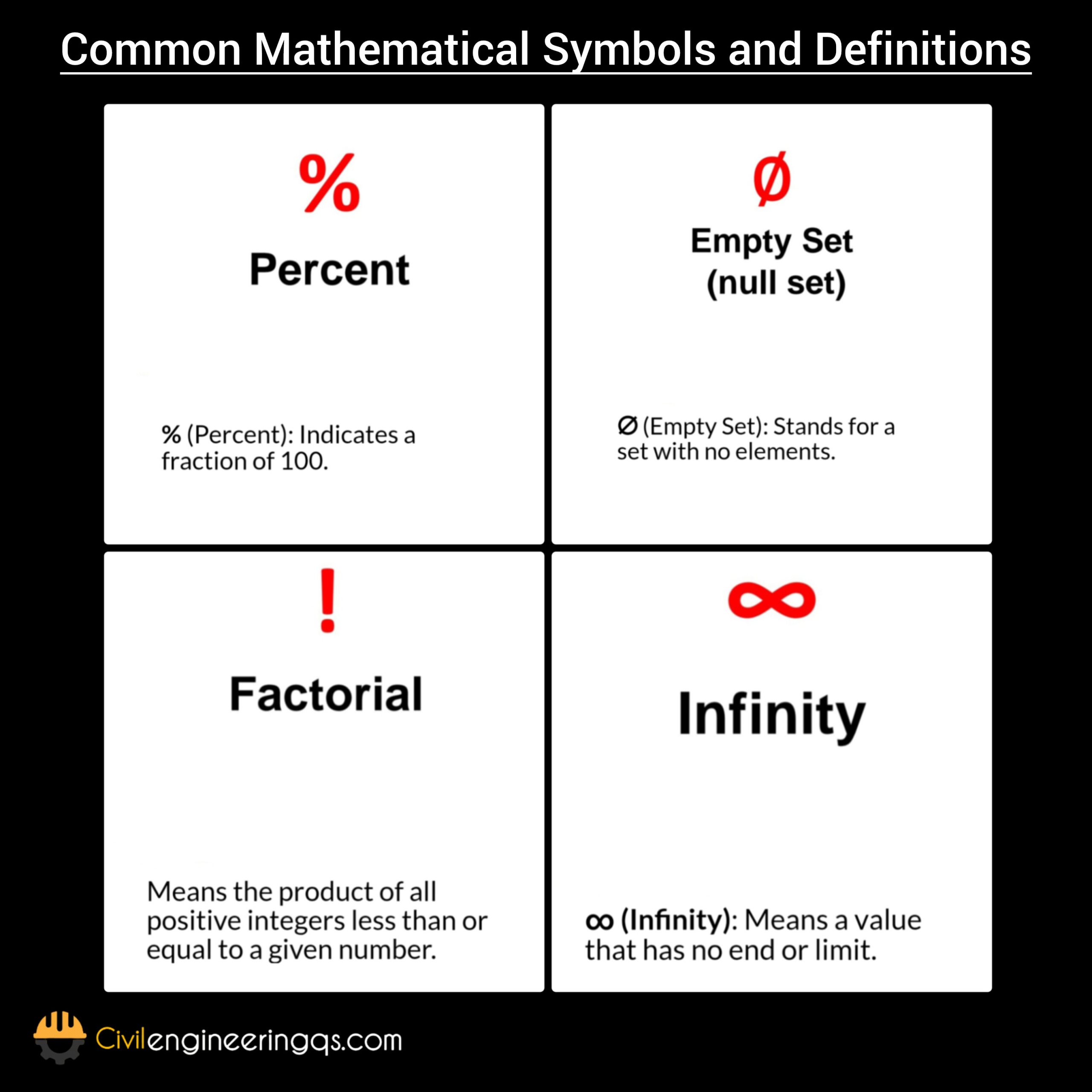
% (Percent): Indicates a fraction of 100.

∅ (Empty Set): Stands for a set with no elements.

Means the product of all positive integers less than or equal to a given number.

∞ (Infinity): Means a value that has no end or limit.
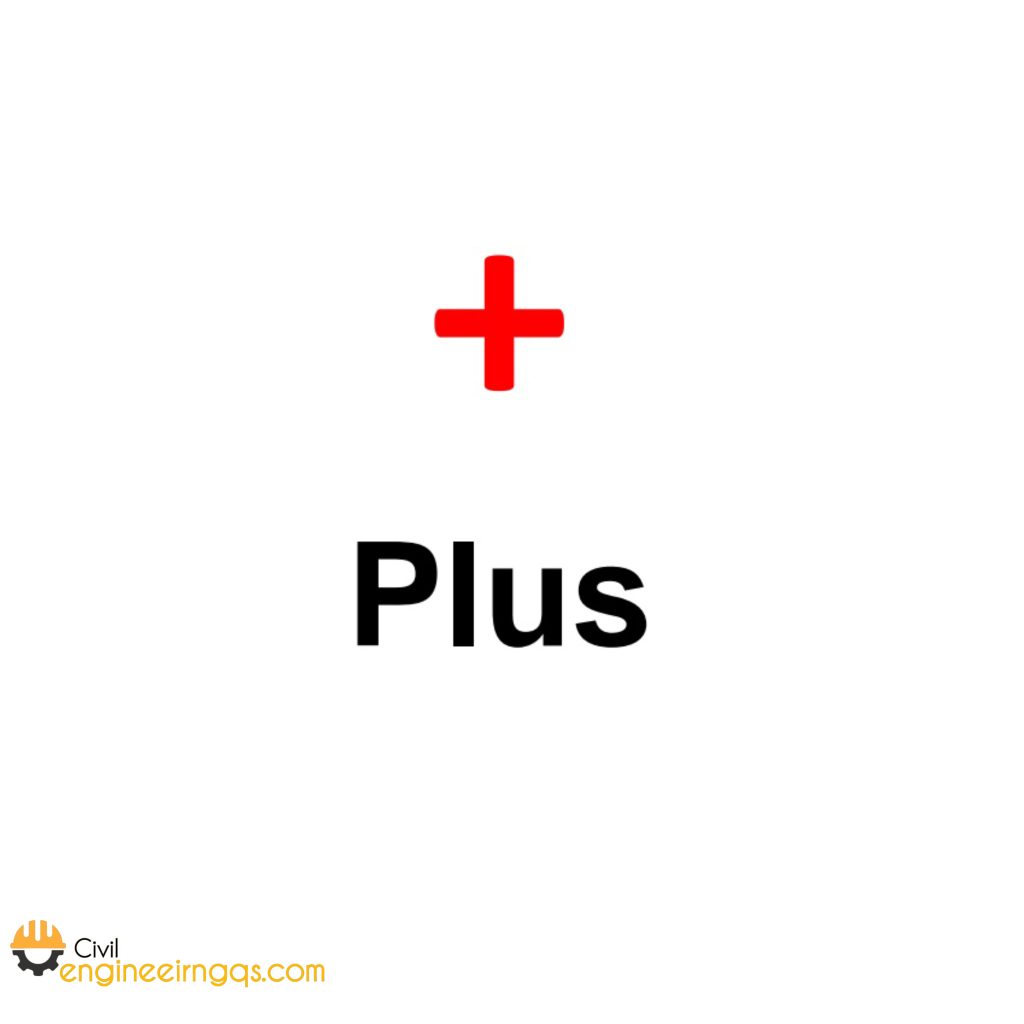
+ (Plus): Used for addition.

− (Minus): Used for subtraction.
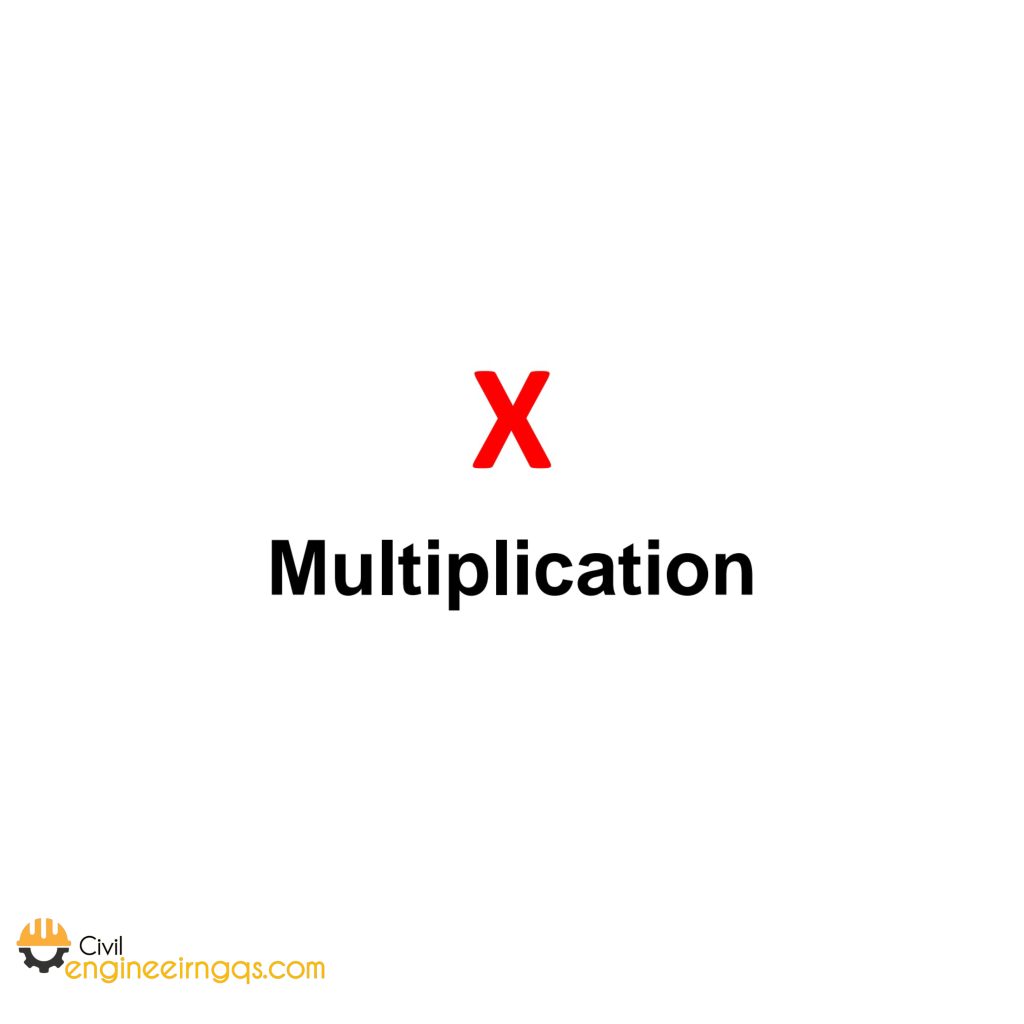
× (Multiplication): Used for multiplying values

÷ (Division): Used for dividing one number by another.
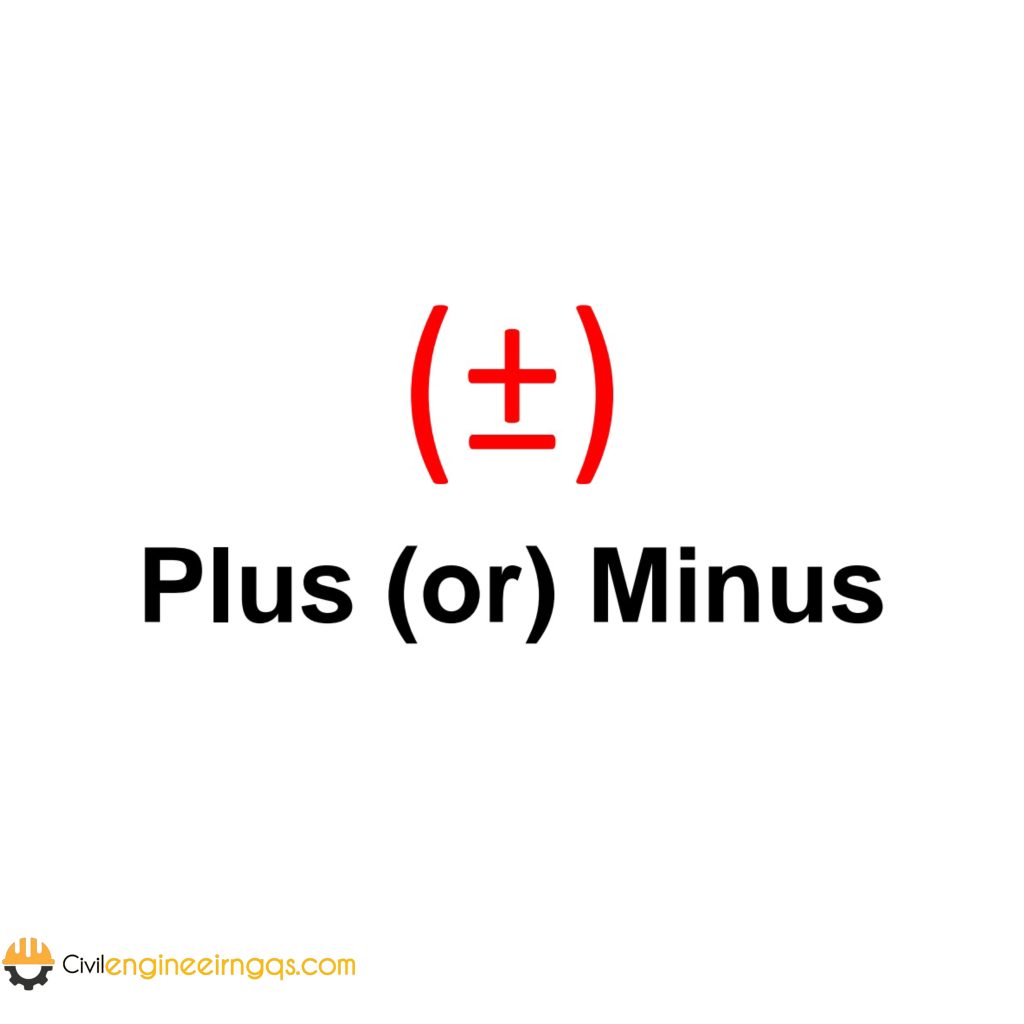
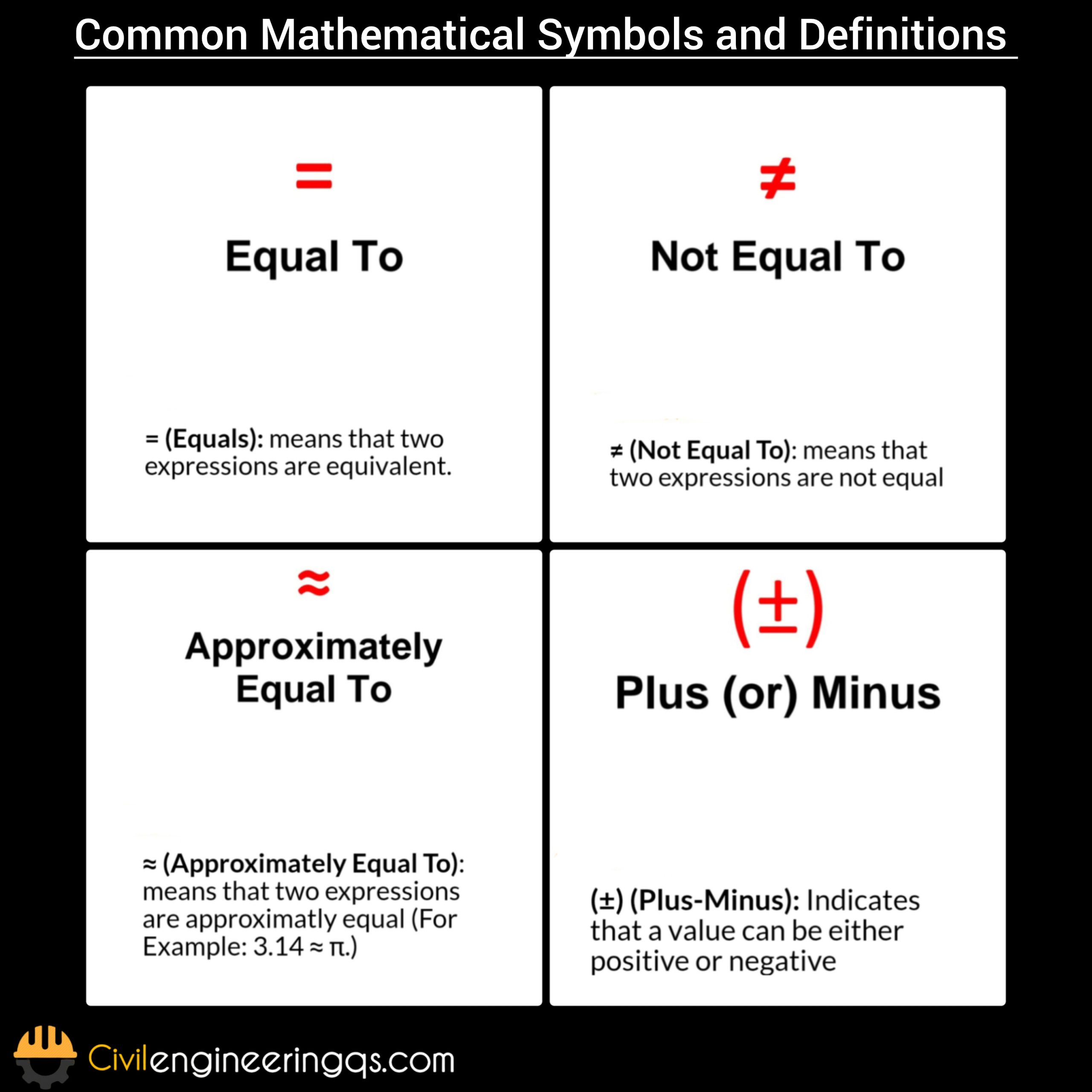
(±) (Plus-Minus): Indicates that a value can be either positive or negative
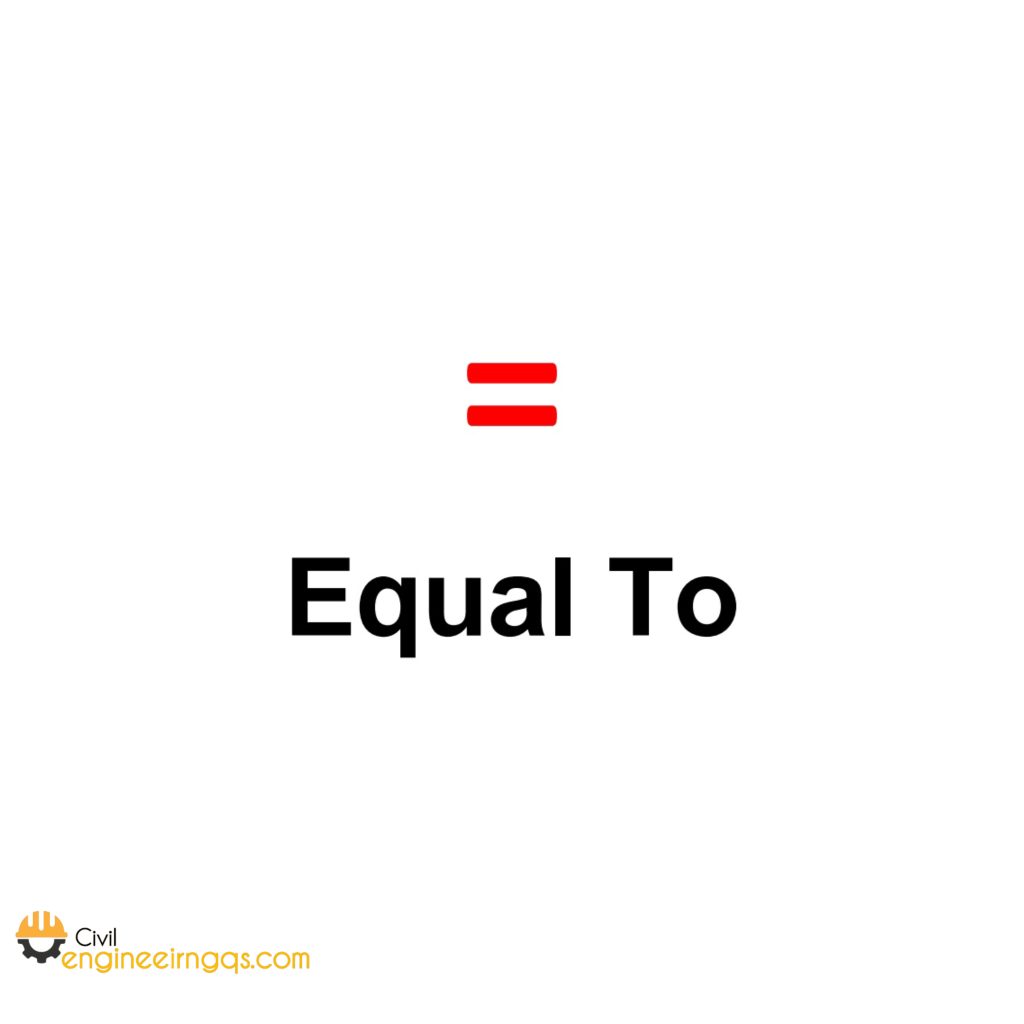
= (Equals): means that two expressions are equivalent.
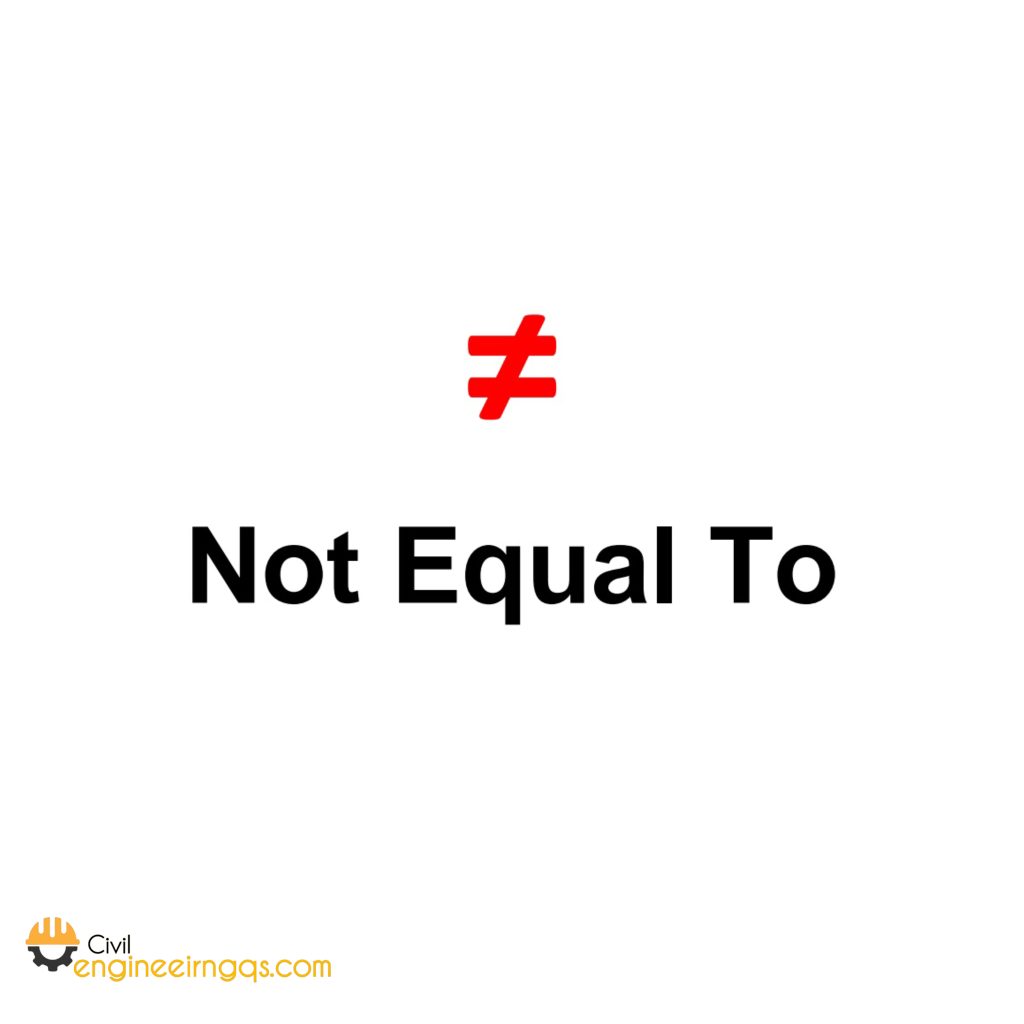
≠ (Not Equal To): means that two expressions are not equal

≈ (Approximately Equal To): means that two expressions are approximatly equal (For Example: 3.14 ≈ π.)

> (Greater Than): Indicates that one value is larger than the other. Example: 7 > 5.

< (Less Than) Indicates that one value is larger than the other. Example: 5 < 7
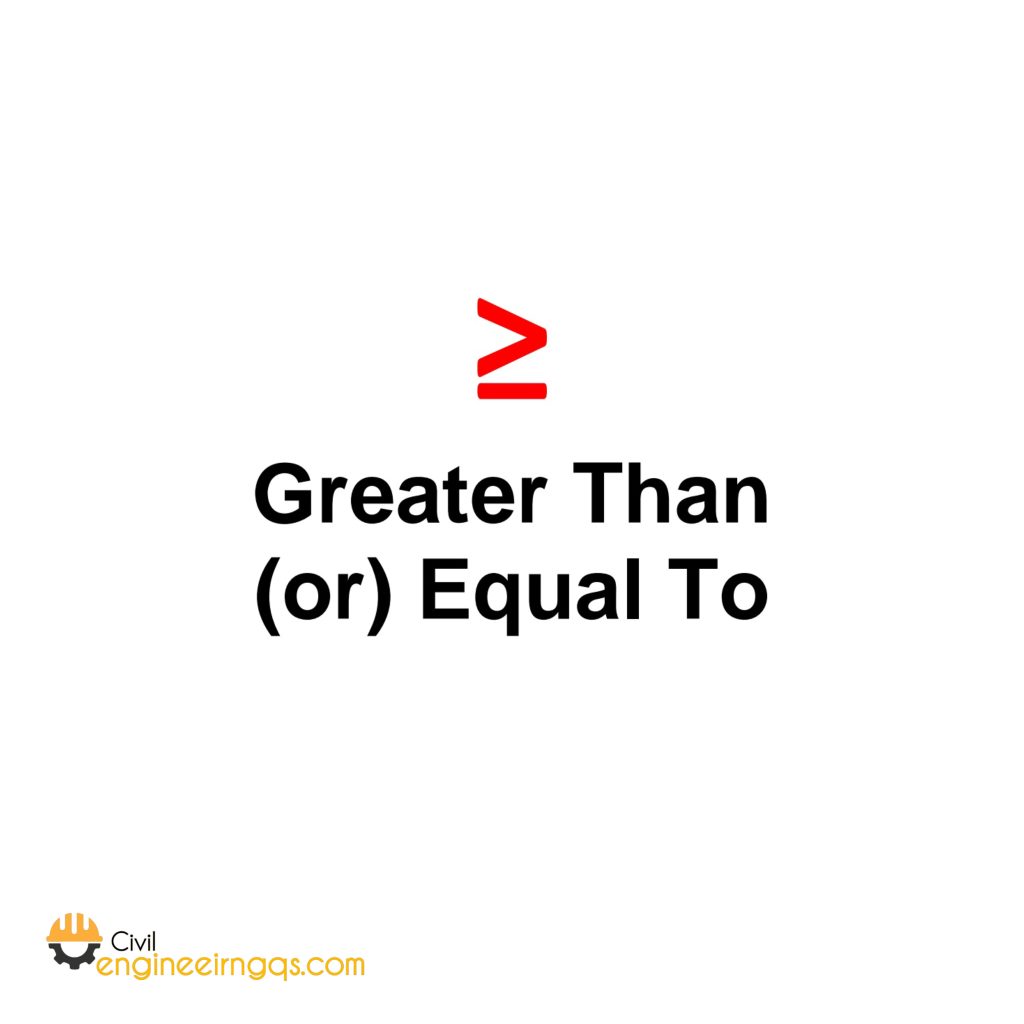
≥ (Greater Than or Equal To): A number is bigger or the same. Example: x ≥ 10 (x can be 10 or more).
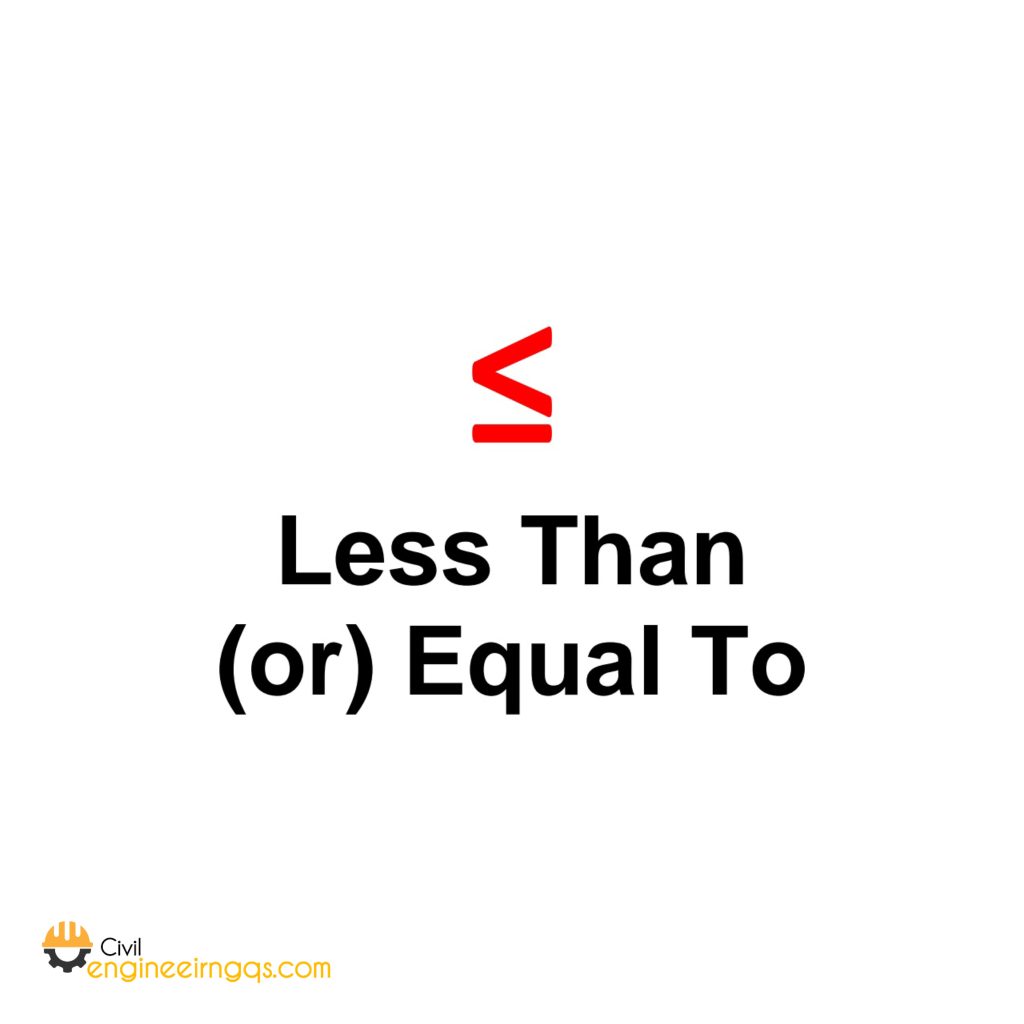
≤ (Less Than or Equal To): A number is smaller or the same. Example: y ≤ 5 (y can be 5 or less).

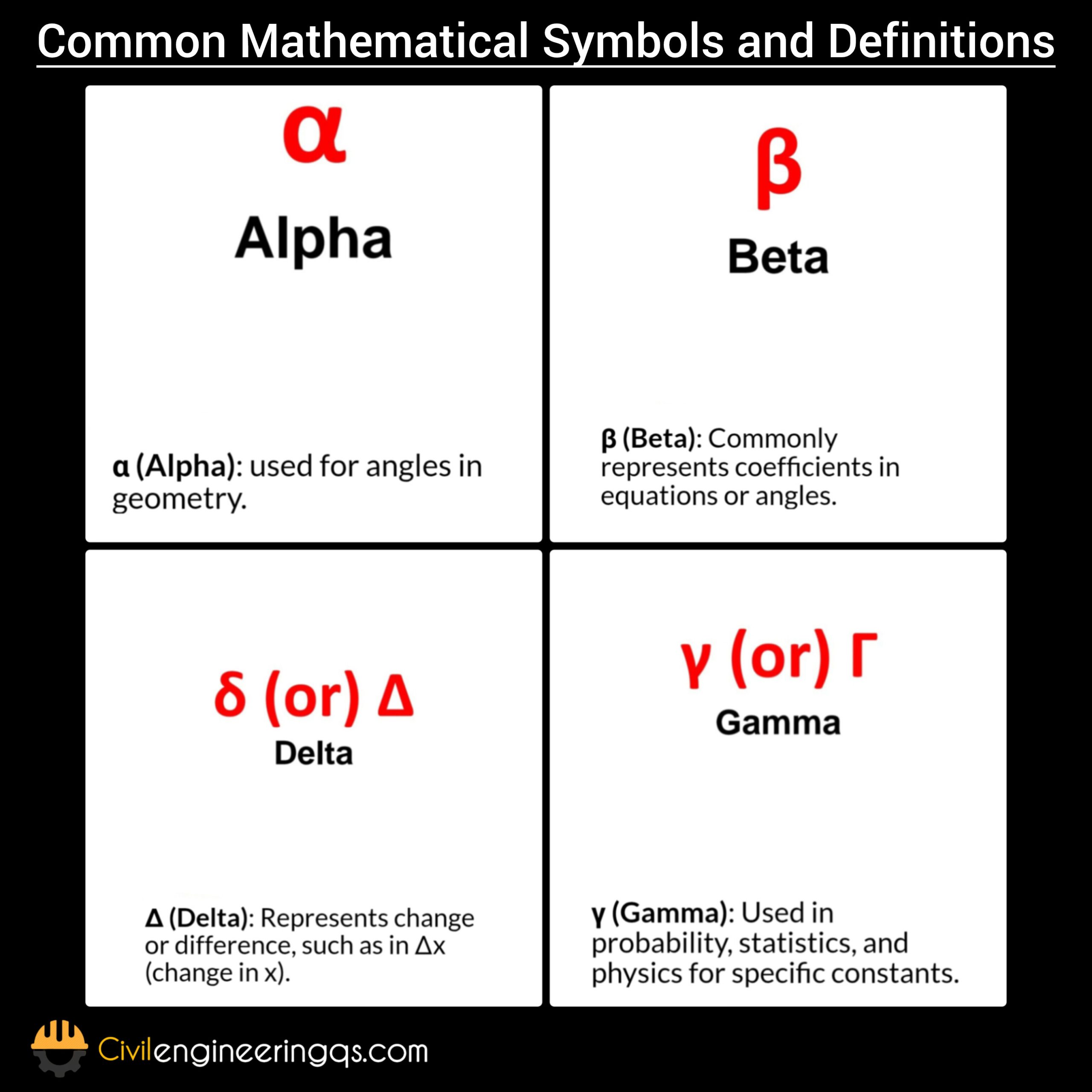
α (Alpha): used for angles in geometry.

β (Beta): Commonly represents coefficients in equations or angles.

γ (Gamma): Used in probability, statistics, and physics for specific constants.

Δ (Delta): Represents change or difference, such as in Δx (change in x).
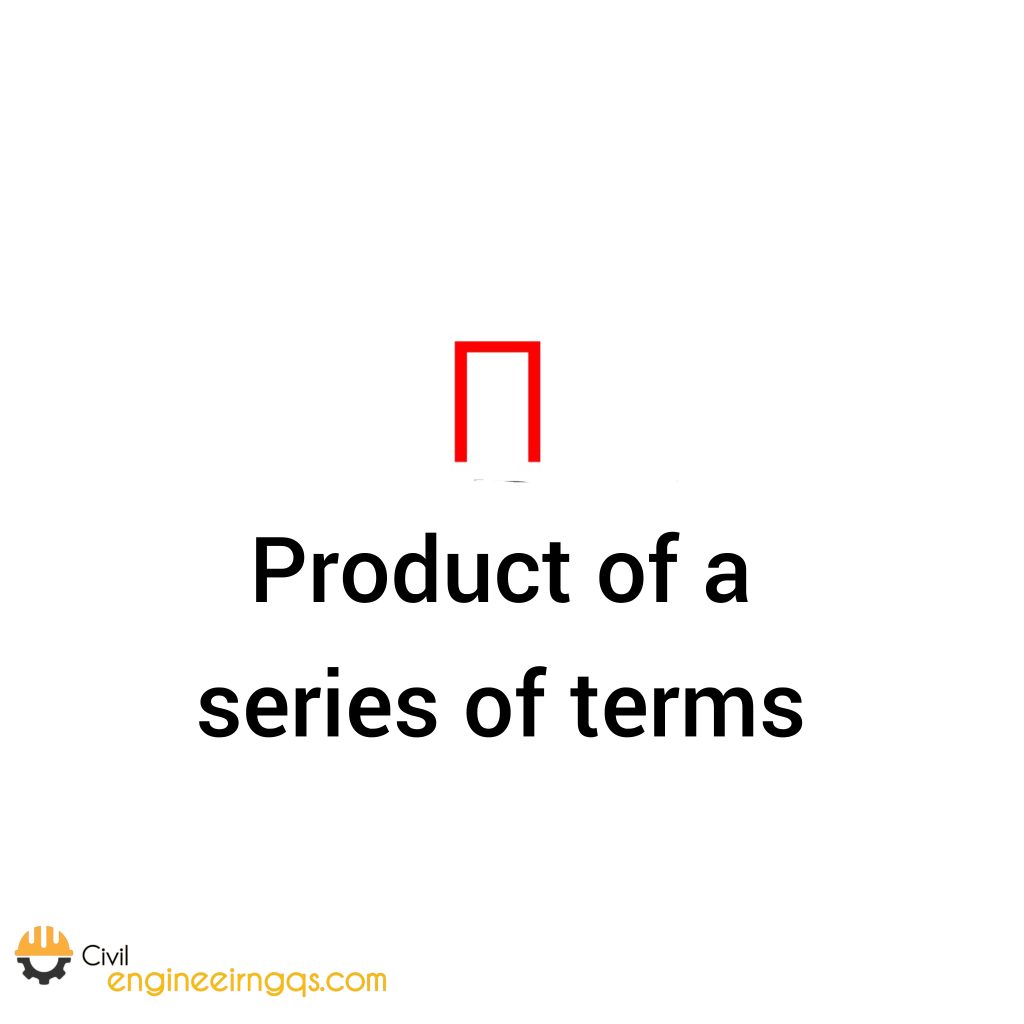
∏ (Product): Means multiplying a series of numbers. Example: 2 × 3 × 4 = 24.

⊥ (Perpendicular): Used in geometry to show two lines meet at a right angle (90°)
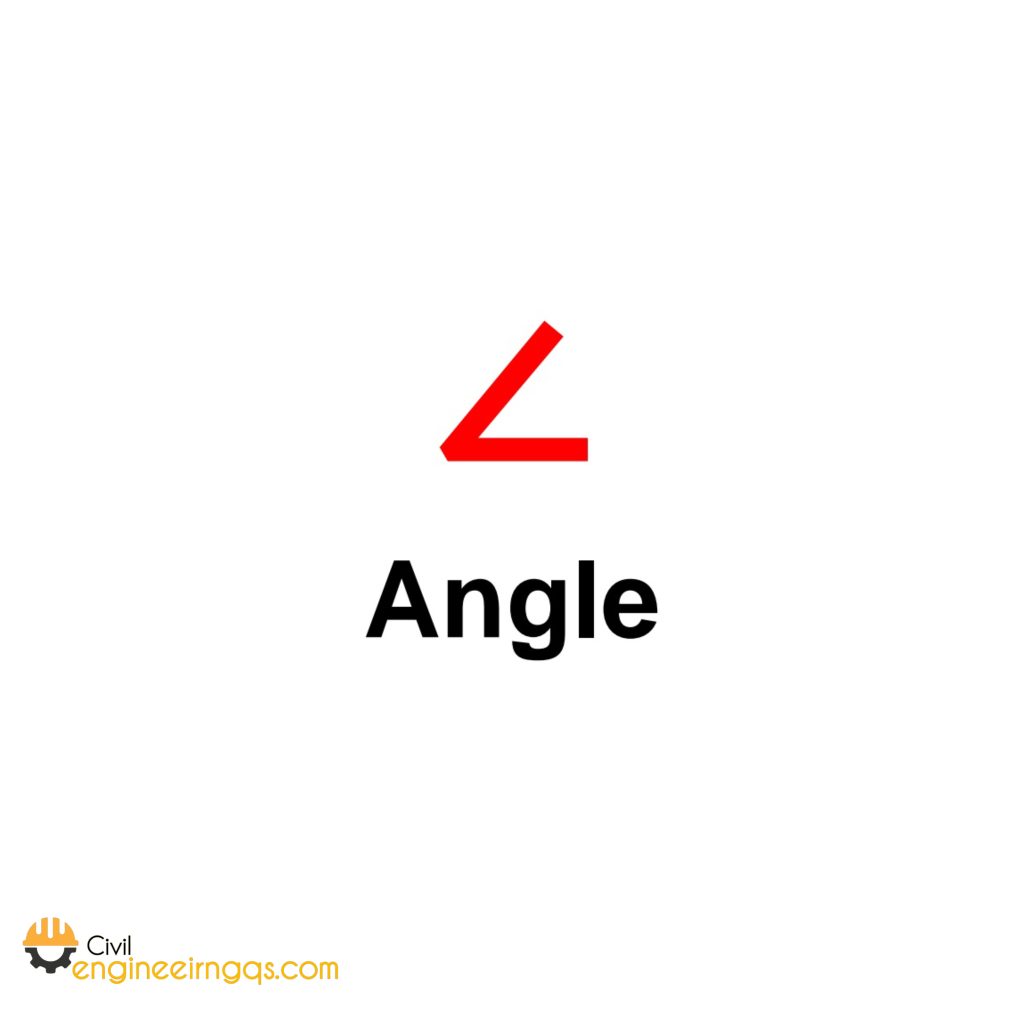
∠ (Angle): Represents an angle. Example: ∠ABC is an angle at point B.

log (Logarithm): Shows how many times a number is multiplied to get another number. Example: log10(100) = 2 (because 10 × 10 = 100).